At the VietAI Summit 2019, Thang Le from the VietAI team, discussed data augmentation and the concept of the backtranslation. He also discussed how to apply this technique in translation from English to Vietnamese.
In machine learning, we have a dataset and mathematical models. Generally, one tries to optimize the machine learning model by fitting data into the model. One of the things that makes machine learning powerful is that we have lots of data. But in some cases, the annotated dataset is very limited. This is where data augmentation comes in.
Data Augmentation: What is it? Why use it?
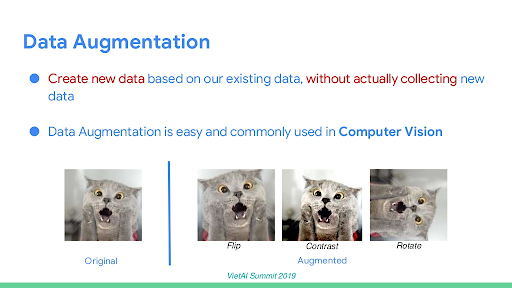
Data augmentation is a great tool to fix the problem of limited data. Data augmentation adds value to base data by adding information derived from internal and external sources. The idea of data augmentation is very simple -- it creates new data from training data without actually collecting the data. For example, in computer vision, we are given input images. To augment the data, we can modify those images by flipping them vertically or horizontally or even changing the color or rotation.
Back-translation Technique

But the story is very different when you apply data augmentation to national language processing (NLP). Because we are working with text, it’s hard to augment that data due to the high complexity in language. This is when back-translation is applied. The idea of back-translation is very simple -- we translate a sentence from the original language to an intermediate language and then translate back to the original language.
A Use-Case From Foody Sentiment Analysis
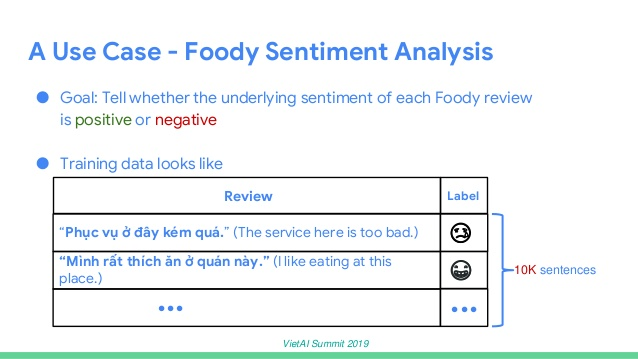
To be more specific about how to do back-translation and how effective it is, Thang used a machine learning problem in Vietnam related to foody sentiment analysis. The goal for sentiment analysis is to tell whether the review is positive or negative. The training data would be many peer reviews and labels. For example, the sentence, “The service here is too bad” is negative and the sentence, “I like eating at this place” is labeled positive. However, this data set was very limited with only 10,000 training samples, so Thang augmented the data using the back-translation technique.
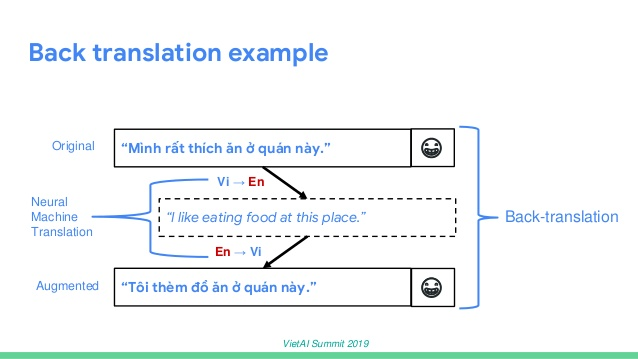
The original sentence here is translated into English. Thang highlighted the input at this place, and then the machine translated it back to Vietnamese so the augmentation would be paraphrased in the same meaning as the original sentence. By using back-translation, we can double the size of the training dataset making it more valuable for later training machine learning models.
To learn more about this data augmentation technique, watch Thang’s full presentation by clicking the video below.
To access all Thang Le’s slides for this presentation, head over to Kambria’s Resource Library. The Resource Library can be accessed for free by community members who own KAT tokens. Simply register for the Kambria platform by clicking “Login/Register” in the top right-hand side of the screen. Then choose “Library” to access materials from the Summit.
About VietAI Summit 2019
More than 450 people attended VietAI Summit 2019, “AI for The Future,” organized by VietAI and Kambria. With a program featuring many reputable guest speakers from big tech companies such as Google Brain, Toyota Research Institute, Kambria, NVIDIA, VinAI Research, Vinbrain, Deakin University, and Vietnam National University HCMC, we received many fresh insights into the exciting state of AI research and application, not just in Vietnam, but also around the world. To receive an invitation to VietAI Summit 2020, Like the VietAI Facebook page and Like the Kambria Facebook page.
To read more tech articles from VietAI Summit 2019, click here.